快速开始
安装 rollup
pnpm add rollup -Drollup 基本命令行
.
├── package.json
└── src
├── index.js
└── util.jsindex.js
import { getRandomNum } from './util.js'
const r = getRandomNum(1, 10)
console.log(r)util.js
/**
* 随机数
* @param {*} min 最小值
* @param {*} max 最大值
* @returns min-max之间的随机整数
*/
export const getRandomNum = (min, max) => {
min = Math.ceil(min)
max = Math.floor(max)
return Math.floor(Math.random() * (max - min + 1)) + min
}
/**
* 深拷贝
* @param obj 需要深拷贝的对象
* @returns 深拷贝对象
*/
export const deepClone = obj => {
if (typeof obj !== 'object' || obj === null) {
return obj
}
const result = Array.isArray(obj) ? [] : {}
for (let key in obj) {
if (obj.hasOwnProperty(key)) {
result[key] = deepClone(obj[key])
}
}
return result
}
export default { getRandomNum, deepClone }查看命令行帮助
npx rollup -hrollup 基本命令行
npx rollup src/index.js --file dist/bundle.js可以看到打印结果基本和源码相差不大,而且,自动做了摇树优化,也就是把没有用到的代码自动的删除了
/**
* 随机数
* @param {*} min 最小值
* @param {*} max 最大值
* @returns min-max之间的随机整数
*/
const getRandomNum = (min, max) => {
min = Math.ceil(min)
max = Math.floor(max)
return Math.floor(Math.random() * (max - min + 1)) + min
}
const r = getRandomNum(1, 10)
console.log(r)而且,我们还能选择编译的格式
对于浏览器:
# 编译为包含自执行函数('iife')的 <script>。
npx rollup src/index.js --file dist/bundle.js --format iife对于 Node.js:
# 编译为一个 CommonJS 模块 ('cjs')
npx rollup src/index.js --file dist/bundle.js --format cjs对于浏览器和 Node.js:
# UMD
npx rollup src/index.js --file dist/bundle.js --format umd配置项
当然一般我们会采用配置项的写法,不会使用命令行,后面也会详细介绍
新建 rollup.config.js
import { defineConfig } from 'rollup'
export default defineConfig({
input: 'src/index.js',
output: {
file: 'dist/bundle.js',
format: 'esm',
name: 'bundle'
}
})
摇树优化(tree shaking)
除了可以使用 ES 模块之外,Rollup 还可以静态分析你导入的代码,并将排除任何实际上没有使用的内容,从上面的引入和最后的打包结果就可以看到,没有使用到的内容直接被删除了。
注意,摇树优化的核心思想是在编译阶段通过静态分析确定代码的使用情况,而不是在运行时。
所以摇树优化一般是建立在ES6 模块化语法基础之上的,ESM 的导入导出是静态的。
CommonJS 模块的导入和导出是动态的,无法在编译阶段静态确定代码的使用情况。一般情况下,摇树优化工具无法在 CommonJS 模块中进行精确的摇树,因为无法静态分析模块间的导入和导出关系。
然而,一些构建工具(如 Webpack)会尝试通过静态分析和启发式方法对 CommonJS 模块进行近似的摇树优化。它们会尽可能地识别出那些可以在编译阶段确定未被使用的代码,并进行剔除。但这种处理方式可能不如对 ES6 模块的优化效果好,且有一定的限制。
摇树优化的原理:
- 静态分析:对 JavaScript 代码进行静态分析,识别出模块的导入和导出关系。
- 标记未使用代码:标记出在导入和导出关系上没有被使用的代码。这些代码可能是模块的导出函数、变量、类等。
- 剔除未使用代码:根据标记结果,构建工具会将未被使用的代码从最终的打包结果中剔除,只保留被使用的部分。
由于是静态分析,所以我们在写代码的时候,需要注意自己的写法,简单来说,尽量的使用最小导入,比如你可以比较一下我们这里导入代码之后,打包的区别:
// 直接默认导入整个对象
import util from './util.js'
const r = util.getRandomNum(1, 10)
console.log(r)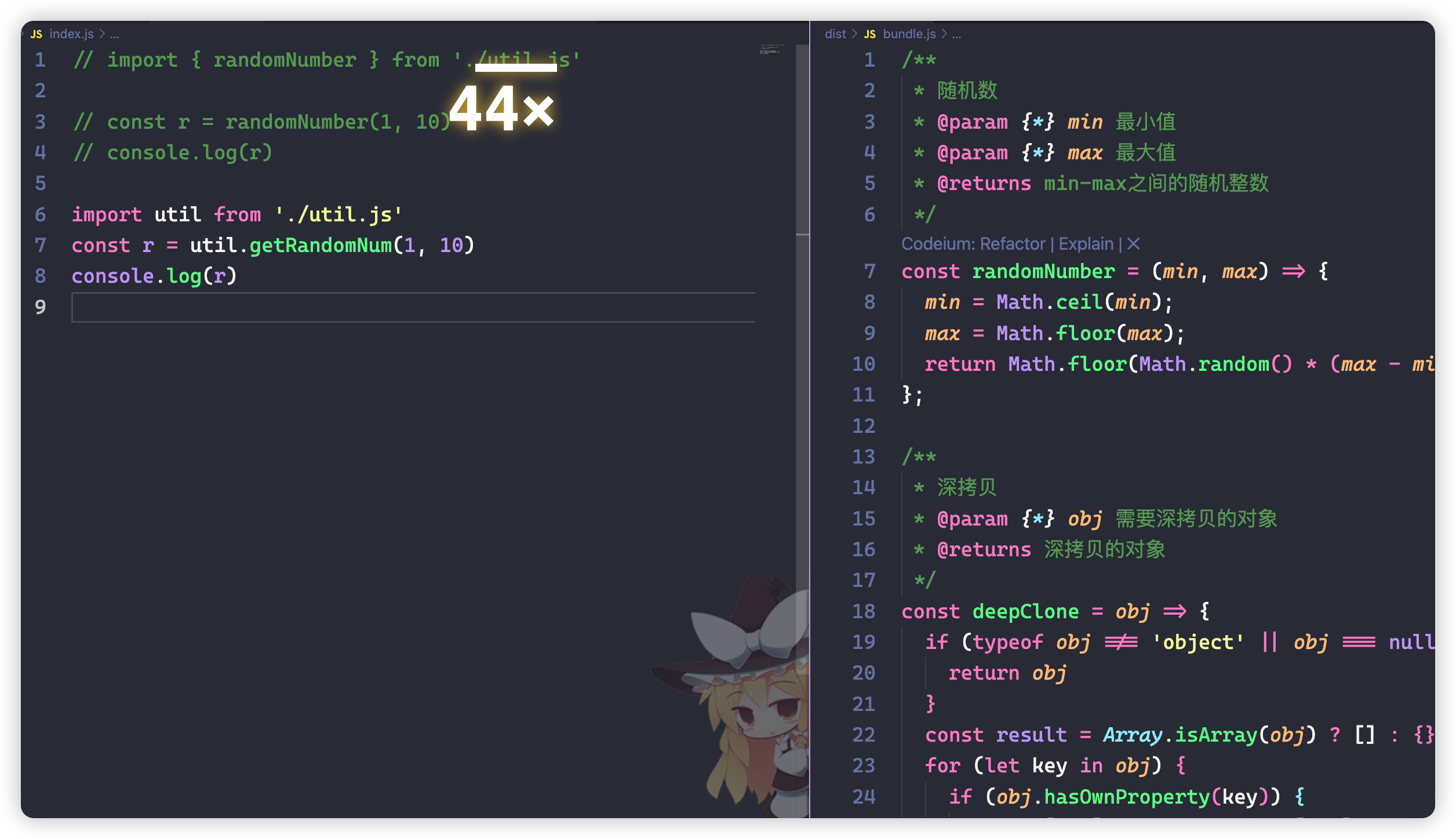
// 具名导入具体的函数
import { getRandomNum } from './util.js'
const r = getRandomNum(1, 10)
console.log(r)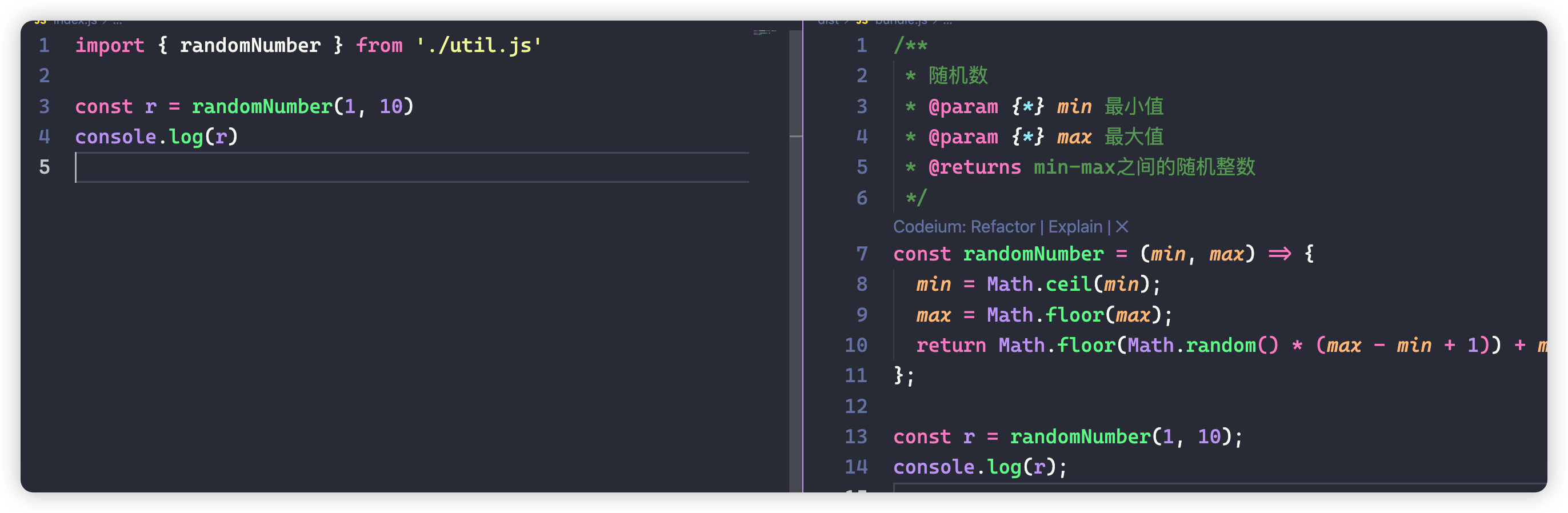
与 webpack 打包的区别
这个打包结果其实就已经和我们熟知的webpack有了很鲜明的区别,我们把 webpack 安装一下试试
pnpm add webpack webpack-cli -D运行 webpack-cli:
# --entry 入口文件 -o 打包文件夹位置 --mode 打包模式
npx webpack --entry ./src/index.js -o dist --mode development/*
* ATTENTION: The "eval" devtool has been used (maybe by default in mode: "development").
* This devtool is neither made for production nor for readable output files.
* It uses "eval()" calls to create a separate source file in the browser devtools.
* If you are trying to read the output file, select a different devtool (https://webpack.js.org/configuration/devtool/)
* or disable the default devtool with "devtool: false".
* If you are looking for production-ready output files, see mode: "production" (https://webpack.js.org/configuration/mode/).
*/
/******/ ;(() => {
// webpackBootstrap
/******/ 'use strict'
/******/ var __webpack_modules__ = {
/***/ './src/index.js':
/*!**********************!*\
!*** ./src/index.js ***!
\**********************/
/***/ (__unused_webpack_module, __webpack_exports__, __webpack_require__) => {
eval(
'__webpack_require__.r(__webpack_exports__);\n/* harmony import */ var _util_js__WEBPACK_IMPORTED_MODULE_0__ = __webpack_require__(/*! ./util.js */ "./src/util.js");\n\nconst r = (0,_util_js__WEBPACK_IMPORTED_MODULE_0__.getRandomNum)(1, 10)\nconsole.log(r)\n\n//# sourceURL=webpack://rollup-demo/./src/index.js?'
)
/***/
},
/***/ './src/util.js':
/*!*********************!*\
!*** ./src/util.js ***!
\*********************/
/***/ (__unused_webpack_module, __webpack_exports__, __webpack_require__) => {
eval(
"__webpack_require__.r(__webpack_exports__);\n/* harmony export */ __webpack_require__.d(__webpack_exports__, {\n/* harmony export */ deepClone: () => (/* binding */ deepClone),\n/* harmony export */ flat: () => (/* binding */ flat),\n/* harmony export */ getRandomNum: () => (/* binding */ getRandomNum)\n/* harmony export */ });\n/**\n * 随机数\n * @param {*} min 最小值\n * @param {*} max 最大值\n * @returns min-max之间的随机整数\n */\nconst getRandomNum = (min, max) => {\n min = Math.ceil(min);\n max = Math.floor(max);\n return Math.floor(Math.random() * (max - min + 1)) + min;\n}\n\n/**\n * 深拷贝\n * @param obj 需要深拷贝的对象\n * @returns 深拷贝对象\n */\nconst deepClone = (obj) => {\n if(typeof obj !== 'object' || obj === null) {\n return obj\n }\n const result = Array.isArray(obj) ? [] : {};\n for(let key in obj) {\n if(obj.hasOwnProperty(key)) {\n result[key] = deepClone(obj[key])\n }\n }\n return result\n}\n\n/**\n * 数组扁平化\n * @param {*} arr 需要扁平化的数组\n * @returns 扁平化后的数组\n */\nconst flat = (arr) => {\n let result = [];\n for (let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {\n if (Array.isArray(arr[i])) {\n result = result.concat(flat(arr[i]));\n } else {\n result.push(arr[i]);\n }\n }\n return result;\n}\n\n\n\n\n//# sourceURL=webpack://rollup-demo/./src/util.js?"
)
/***/
}
/******/
}
/************************************************************************/
/******/ // The module cache
/******/ var __webpack_module_cache__ = {}
/******/
/******/ // The require function
/******/ function __webpack_require__(moduleId) {
/******/ // Check if module is in cache
/******/ var cachedModule = __webpack_module_cache__[moduleId]
/******/ if (cachedModule !== undefined) {
/******/ return cachedModule.exports
/******/
}
/******/ // Create a new module (and put it into the cache)
/******/ var module = (__webpack_module_cache__[moduleId] = {
/******/ // no module.id needed
/******/ // no module.loaded needed
/******/ exports: {}
/******/
})
/******/
/******/ // Execute the module function
/******/ __webpack_modules__[moduleId](module, module.exports, __webpack_require__)
/******/
/******/ // Return the exports of the module
/******/ return module.exports
/******/
}
/******/
/************************************************************************/
/******/ /* webpack/runtime/define property getters */
/******/ ;(() => {
/******/ // define getter functions for harmony exports
/******/ __webpack_require__.d = (exports, definition) => {
/******/ for (var key in definition) {
/******/ if (__webpack_require__.o(definition, key) && !__webpack_require__.o(exports, key)) {
/******/ Object.defineProperty(exports, key, { enumerable: true, get: definition[key] })
/******/
}
/******/
}
/******/
}
/******/
})() /* webpack/runtime/hasOwnProperty shorthand */
/******/
/******/
/******/
;(() => {
/******/ __webpack_require__.o = (obj, prop) => Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(obj, prop)
/******/
})() /* webpack/runtime/make namespace object */
/******/
/******/
/******/
;(() => {
/******/ // define __esModule on exports
/******/ __webpack_require__.r = exports => {
/******/ if (typeof Symbol !== 'undefined' && Symbol.toStringTag) {
/******/ Object.defineProperty(exports, Symbol.toStringTag, { value: 'Module' })
/******/
}
/******/ Object.defineProperty(exports, '__esModule', { value: true })
/******/
}
/******/
})()
/******/
/************************************************************************/
/******/
/******/ // startup
/******/ // Load entry module and return exports
/******/ // This entry module can't be inlined because the eval devtool is used.
/******/ var __webpack_exports__ = __webpack_require__('./src/index.js')
/******/
/******/
})()当然我们可以选择生成模式进行打包
npx webpack --entry ./src/index.js -o dist --mode production;(() => {
'use strict'
const o = ((t = 1), (a = 10), (t = Math.ceil(t)), (a = Math.floor(a)), Math.floor(Math.random() * (a - t + 1)) + t)
var t, a
console.log(o)
})()现在打包出来的内容就直接是压缩之后的代码了
配置文件
Rollup配置文件是一个 ES 模块。通常,它被称为 rollup.config.js 或 rollup.config.mjs,并位于项目的根目录中。它导出一个默认对象,其中包含所需的选项:
export default {
input: 'src/index.js',
output: {
file: 'dist/bundle.js',
format: 'esm'
}
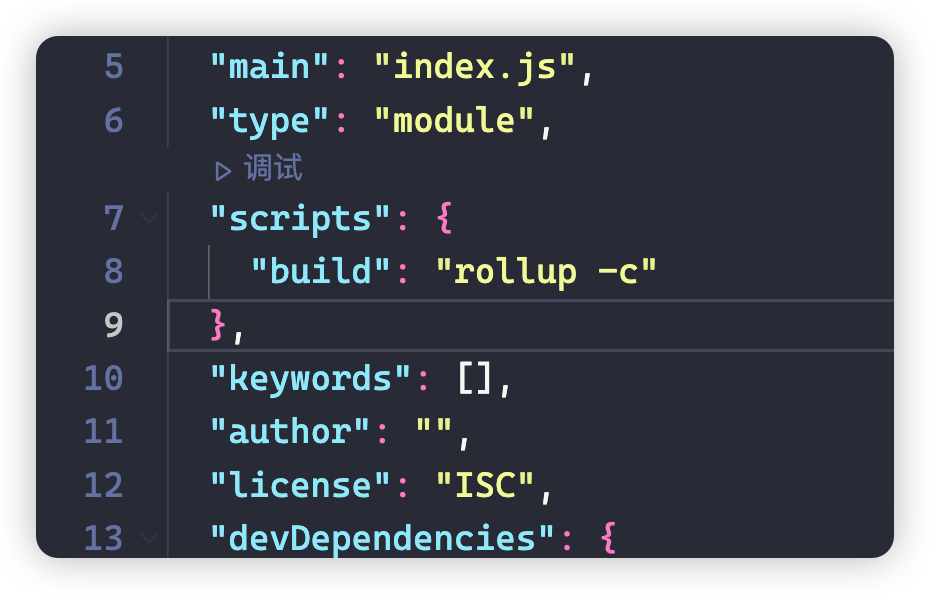
}注意:nodejs 环境下要运行 esm 模块化的内容,要么文件名后缀处理为**.mjs**,要么 package.json 文件中配置**"type":"module"**,因为 Rollup 将遵循 Node ESM 语义。
要运行配置文件,可以在命令行执行
npx rollup -c或者直接在package.json文件中配置script脚本
{
......
"type":"module",
"scripts": {
"dev":"rollup -c"
},
......
}配置时的智能提示
由于 Rollup 随附了 TypeScript 类型定义,因此你可以使用 JSDoc 类型提示来利用你的 IDE 的智能感知功能:
/**
* @type {import('rollup').RollupOptions}
* @description: rollup配置文件
*/
export default {
input: 'src/index.js',
output: {
file: 'dist/bundle.js',
format: 'umd',
name: 'bundle'
}
}或者,你可以使用 defineConfig 辅助函数,它应该提供无需 JSDoc 注释即可使用智能感知的功能:
import { defineConfig } from 'rollup'
export default defineConfig({
input: 'src/index.js',
output: {
file: 'dist/bundle.js',
format: 'umd',
name: 'bundle'
}
})